Bài tập bổ trợ Tiếng Anh Lớp 10 Global Success - Unit 6: Gender equality
Bạn đang xem tài liệu "Bài tập bổ trợ Tiếng Anh Lớp 10 Global Success - Unit 6: Gender equality", để tải tài liệu gốc về máy hãy click vào nút Download ở trên.
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Bài tập bổ trợ Tiếng Anh Lớp 10 Global Success - Unit 6: Gender equality
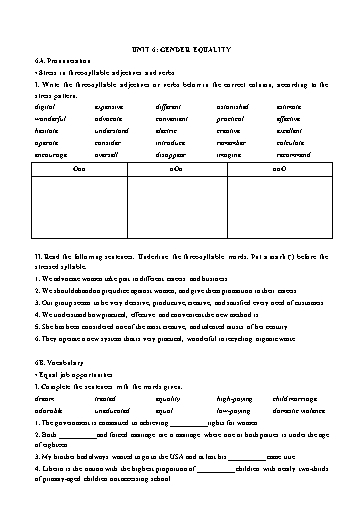
5. As part-time, __________ workers, the women earned very little. 6. A(n) __________ job satisfies one’s basic needs and fulfils one’s dreams like buying homes or cars. 7. Prevention of __________ involves providing equal economic opportunities to men and women. 8. Have you seen their new baby - she’s simply __________ ! 9. In an ideal world, would everyone get __________ equally? 10. Women have yet to achieve full __________ with men in the workplace. • Gender equality II. Complete the sentences with the words given. equal domestic violence treated surgeon child marriage gender low-paying dream 1. __________ ends the childhood of girls, and they are forced into adulthood before they are physically and mentally ready. 2. The __________ told reporters that Sara was making good progress after the heart transplant. 3. In higher education, women are __________ in numbers to men. 4. Last year her __________ came true and she was offered a chance to study in America. 5. The job centre seems to list only __________ temporary jobs. 6. __________ is any behaviour the purpose of which is to gain control over a spouse or a partner. 7. All people should be __________ equally, whatever their age or sex. 8. There many __________ differences in attitudes to paid work. III. Complete the sentences with the correct prepositions. 1. The purpose of the law is to end discrimination __________ workplace. 2. All over the world women are demanding equal opportunities __________ education and work. 3. The law puts a limitation __________ the number of hours children can work. 4. She dreamed __________ becoming a scientist. 5. Her maternity leave prevented her __________ getting the promotion. 6. Some people aren’t fully aware __________ gender discrimination in society. 7. Elderly parents are dependent __________ their children either male or female __________ physical care. 8. The government must ensure equality __________ opportunity __________ all children. 9. The career is his family tradition, passing __________ from generation to generation. 10. Parents should set a good example __________ their children. IV. Fill in each blank with the correct word below. Each word has to be used only once. freedom status feminist opportunities education gender quality responsibility injustice women Famous Women Equality Quotes 1. “My goal is not to get a Nobel Peace Prize.... My goal is to get peace and my goal is to see __________ of every child.” (Malala Yousafzai) 5. The __________ of women in the labour market in Iceland is one of the highest in the world, (participate) VII. Choose the correct word. 1. The least equal / equally / equality country in the world for women, ranking 145 th, was Yemen, where only 55% of women can read and only 6% attend college. 2. UNICEF says that access to education is one of the biggest challenges / questions / refusals facing children in Yemen today, especially girls. 3. Until now, the high cost of courses / lectures / schooling has discouraged or prevented poor parents from having their children, especially girls, educated. 4. Moreover, a miss / need / lack of female teachers contributes to low enrolment of girls in schools. 5. UNICEF is now providing schools and families with / for / of educational supplies to help lower costs. 6. Through a joint study / project / survey involving the World Bank, UNICEF hopes to help the government provide all children with textbooks at the beginning of each school year. 7. UNICEF is working both nationally and regionally to teach / inform / educate the public on the importance of educating girls. 8. The gender equality / inequality / fairness in education in Yemen is among the highest in the world - it’s bad news to girls there. 6C. Grammar • Passive voice with modals I. Rewrite the active sentences in the passive. 1. People won’t use maps in the future. Maps_______________________________________________________________________. 2. Manufacturers will build cars with a GPS system. Cars _______________________________________________________________________. 3. People won’t need travel agencies. Travel agencies ______________________________________________________________. 4. Parents will plan family holidays online. Family holidays ______________________________________________________________. 5. Factories won’t manufacture televisions any more. Televisions __________________________________________________________________. 6. Manufacturers will develop bigger computer screens. Bigger computer screens _______________________________________________________. II. Complete the text. Use the future active or passive, affirmative or negative. Today, Google is the most popular search engine in the world, but in the future traditional search engines 1__________ (become) less and less popular. Why? Because typed words 2__________ (not use) by people any more. Instead, pictures 3__________ (take) and used to find out information. Imagine these scenarios: sledding and climbing trees. She lived with her grandparents until she was ten. At ten she moved back with her parents and her younger sister, Muriel. 2. _____________________________________ Amelia saw her first airplane at the 1908 Iowa State Fair. At this fair, there was a stunt- flying exhibition, and it fascinated Amelia. It was here, as she watched these planes twirling and swooshing, that Amelia fell in love with the idea of flying. Amelia actually had to wait thirteen years to take her first ride in a plane, and just six months after that, she bought her first plane. It was bright yellow and she called it Canary. 3. _____________________________________ Amelia was very competitive, and entered many flying contests over the next several years. She continually broke the records of other pilots. To mention just a few: In June of 1928, she became the first woman to fly across the Atlantic. In May of 1932, she became the second person to fly solo across the Atlantic. From August 24 to 25, 1932, she flew a solo nonstop flight from the west coast of the United States to the east coast, making her the first woman to do that. From April 24 to 25, 1935, she was the first person to fly solo from Hawaii to California. 4. _____________________________________ At the age of forty, in 1937, Amelia Earhart wanted to be the first woman to fly around the world. She and her navigator took off from Oakland, California, and flew to Miami, then through the Caribbean to Brazil and through Africa to India. After India, they flew to Bangkok, Indonesia, Australia, and then Papua New Guinea. From Papua New Guinea, they flew toward Howard Island, 2,200 miles away. They never arrived, and despite extensive searches, they were never found. No one knows for sure what happened to Amelia and her navigator, but the world knows that Amelia is one of the most important and influential pilots in history. II. Read the passage, and decide whether the following statements are true (T), false (F), or not given (NG). Malala Yousafzai was born on July 12, 1997, in Mingora, Pakistan. As a young girl, she demanded that girls should be allowed to receive an education, which resulted in the Taliban issuing a death threat against her. After the Taliban began attacking girls’ schools in Swat, Malala gave a speech whose title was, “How dare the Taliban take away my basic right to education?” In early 2009, Yousafzai began blogging for the BBC about living under the Taliban’s threats to deny her an education. Yousafzai continued to speak out about her right, and the right of all women, to an education. She was shot in the head by a Taliban gunman in 2012, but survived. The shooting resulted in a massive support for Yousafzai, which continued during her recovery. She gave a speech at the United Nations on her 16th birthday, in 2013. She has also written an autobiography “I Am Malala: The Girl Who Stood Up for Education and Was Shot by the Taliban”, which was released in October 2013. The mothers, when work, become an inspiration for their kids as they look up to their mums and say that they aspire to be like their mums in the near future. Working mums not only work but also look after their children without any difficulty. So such kids need to get an inspiration at home, and they also learn to do hard work in their life. Task 1. Match words 1-5 with definitions A-G, writing the answer in each blank. There are two extra definitions. 1. intact (adj) _____ A. to make someone have a strong feeling 2. inculcate (v) _____ B. to remember something by doing it so often 3. inspiration (n) _____ C. to respect or admire (someone) 4. look up to (v) _____ D. to have a strong desire to do something 5. aspire (v) _____ E. complete and in the original state F. someone or something that gives you ideas for doing something G. to fix beliefs or ideas in someone’s mind Task 2. Read the passage again, and answer the questions below. 1. Why does every woman at home prefer to go to work? ______________________________________________________________________________ 2. Why do the children of working mothers become smarter, more active, and more independent? ______________________________________________________________________________ 3. How can children learn good habits from their fathers at home? ______________________________________________________________________________ 4. What financial benefits does a working mother bring to her family? ______________________________________________________________________________ 5. Why do working mothers become an inspiration for their children? ______________________________________________________________________________ IV. Read the passage, and choose the correct answer A, B, C or D for each question. A pioneer leader for women’s rights, Susan Anthony became one of the leading women reformers of the 19th century. In Rochester, New York, she began her first public crusade on behalf of temperance, the habit of not drinking alcohol. The temperance movement dealt with the abuses of women and children who suffered from alcoholic husbands. Also, she worked tirelessly against slavery and for women’s rights. Anthony helped write the history of woman suffrage. At the time Anthony lived, women did not have the right to vote. Because she voted in the 1872 election, a US official arrested Anthony. She hoped to prove that women had the legal right to vote under the provisions of the 14th and 15th Amendments to the Constitution. At her trial, a hostile federal judge found her guilty and fined her $100, which she refused to pay. Anthony did not work alone. She worked with reformers of women’s rights such as Elizabeth Cady Stanton and Amelia Bloomer. Susan worked for the American Anti-Slavery Society with Frederick Douglas, a fugitive slave and black abolitionist. ever to win two Nobel Prizes in different subjects, physics and chemistry. Maria Sklodowska was born in Warsaw, Poland in 1867. Maria went to Paris to study mathematics and physics. She met Pierre Curie, who was a well-known scientist. They got married in 1895. Marie Curie is famous for her work on radiation, which she named ‘radioactivity’. She used the word ‘radioactive’ to describe substances that produce rays. Scientists already knew about the existence of ‘X-rays’, but they didn’t know what they were. Marie Curie’s research showed that these radioactive rays come from atoms. She discovered polonium and radium, which are both radioactive elements. Her research was essential for the use of X-rays in medicine. She knew that doctors could use X-rays to reveal broken bones. During World War One, she organized twenty mobile X-ray units to help doctors. Marie also discovered that doctors could use another radioactive element, called radon, to treat cancer. Marie Curie faced great opposition from male scientists in France, but she never gave up her research. She died in 1934 from leukemia that she developed because of her exposure to radiation. In those days, the health dangers of radioactivity were unknown. Her daughter Irene Curie was also a great scientist who won the Nobel Prize for chemistry in 1935. Task 1. Complete the notes about Marie Curie. Occupation: ______________________________________ Nationality: ______________________________________ Famous for: ______________________________________ Task 2. Find these words in the text, and match them to their definitions. 1. elements __________ a. being affected by something 2. reveal __________ b. stopped doing something 3. treat __________ c. make something known 4. gave up __________ d. the basic substances 5. exposure __________ e. tried to make a sick person well again Task 3. Answer the questions. 1. What have more women done in the last 100 years? ________________________________________________________________________________ 2. How many subjects did Marie Curie win Nobel prizes for? ________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Why did she go to Paris? ________________________________________________________________________________ 4. What did she discover about radioactive rays? ________________________________________________________________________________ 5. What radioactive elements did she discover? ________________________________________________________________________________ 6. What did she do during World War One? ________________________________________________________________________________ 7. How did she die? ________________________________________________________________________________ 6E. Speaking • Everyday English I. Choose the correct response. Then practise the short exchanges in pairs. 1. A: Women should stay at home and take B: a/ I think they can follow their careers and care of the family. interests outside the family. b/ I don’t think men are more hard-working. 2. A: Women won’t become CEOs B: a/ Why not? They are also good leaders. b/ Why not? Men are better leaders than women. 3. A: Nowadays women get equal job B: a/ They can have more breaks than men. opportunities as men. b/ But they don’t get equal pay. 4. A: Do you agree that doing housework is B: a/ But we can use labour-saving devices. very boring? b/ Women can do that by themselves. 5. A: Housewives are often financially B: a/ Not really. That’s true. dependent on their husbands. b/ You bet! 6. A: Men should share household chores with B: a/ No, I guess so. their wives. b/ I agree with you. 7. A: Do you think women in Korea get good B: a/ I hope not. gender equality? b/ I don’t think so. 8. A: Oh, most of our teachers are female! B: a/ Yes, women are better at taking care of children. b/ Yes, women should be encouraged to work outside the home. 9. A: Can you see any benefits of a working B: a/ She’ll have less time to take care of her mother? children. b/ She can set a good example for the the children. 10. A: Why should girls get higher education? B: a/ In order to do household chores better. b/ In order to get good jobs and promotion. • Career choices II. Use the notes and useful expressions to complete the dialogue to offer the career choices. Realistic: Realistic people like to work with things they can see or touch. Job matches: carpenter, chef, nurse, pilot Investigative: People of this type like research and study, rather than leading groups of people. Job matches: computer programmer, surgeon
File đính kèm:
 bai_tap_bo_tro_tieng_anh_lop_10_global_success_unit_6_gender.docx
bai_tap_bo_tro_tieng_anh_lop_10_global_success_unit_6_gender.docx

