Bài tập bổ trợ Tiếng Anh Lớp 11 Global Success - Unit 10: The ecosystem (Có file nghe và đáp án)
Bạn đang xem tài liệu "Bài tập bổ trợ Tiếng Anh Lớp 11 Global Success - Unit 10: The ecosystem (Có file nghe và đáp án)", để tải tài liệu gốc về máy hãy click vào nút Download ở trên.
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Bài tập bổ trợ Tiếng Anh Lớp 11 Global Success - Unit 10: The ecosystem (Có file nghe và đáp án)
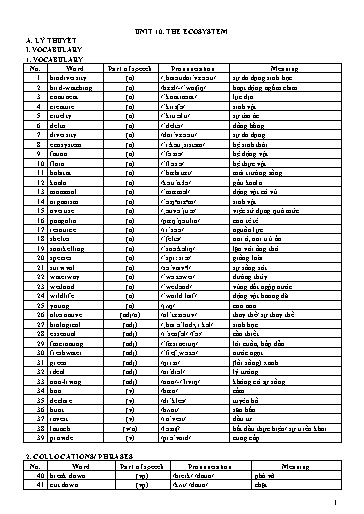
42. run out (of) (vp) /rʌn/ /aʊt/ /ɒv/ cạn kiệt 43. located in (phrase) /ləʊˈkeɪtɪd/ /ɪn/ nằm ở 44. native to (adj) /ˈneɪtɪv/ /tuː/ tự nhiờn, bản địa 45. home to (phrase) /həʊm/ /tuː/ là nhà của 46. loss of biodiversity (phrase) /lɒs/ /əv/ sự mất đa dạng sinh học /ˌbaɪəʊdaɪˈvɜːsəti/ 47. carbon footprint (np) /ˈkɑːbᵊn/ /ˈfʊtprɪnt/ lượng khớ thải cỏc bon 48. coral reef (np) /ˈkɒrəl/ /riːf/ rạn san hụ 49. fishing cat (np) /ˈfɪʃɪŋ/ /kổt/ mốo cỏ 50. food chain (np) /fuːd/ /ʧeɪn/ chuỗi thức ăn 51. food security (np) /fuːd/ /sɪˈkjʊərəti/ an ninh lương thực 52. forest fire (np) /ˈfɒrɪst/ /ˈfaɪə/ chỏy rừng 53. fossil fuel (np) /ˈfɒsᵊl/ /ˈfjuːəl/ nhiờn liệu hoỏ thạch 54. great spotted eagle (np) /ɡreɪt/ /ˈspɒtɪd/ /ˈiːɡᵊl/ đại bàng đốm lớn 55. green job (adj-n) /ɡriːn/ /ʤɒb/ cụng việc liờn quan đến mụi trường 56. life expectancy (np) /laɪf/ /ɪkˈspektᵊnsi/ tuổi thọ 57. living things (adj-n) /ˈlɪvɪŋ/ /θɪŋz/ những sinh vật sống 58. mangrove forest (np) /ˈmổŋɡrəʊv/ /ˈfɒrɪst/ rừng ngập mặn 59. marine reserve (np) /məˈriːn/ /rɪˈzɜːv/ khu bảo tồn biển 60. national park (adj-n) /ˈnổʃᵊnᵊl/ /pɑːk/ rừng quốc gia 61. natural resources (adj-n) /ˈnổʧrəl/ /rɪˈsɔːsɪz/ tài nguyờn thiờn nhiờn 62. no-take zone (np) /nəʊ/-/teɪk/ /zəʊn/ vựng được bảo tồn (khụng được lấy đi thứ gỡ) 63. oil drilling (np) /ɔɪl/ /ˈdrɪlɪŋ/ sự khoan dầu 64. raw material (adj-n) /rɔː/ /məˈtɪərɪəl/ nguyờn liệu thụ 65. scuba diving (np) /ˈskuːbə/ /ˈdaɪvɪŋ/ mụn lặn 66. tropical forest (adj-n) /ˈtrɒpɪkəl/ /ˈfɒrɪst/ rừng nhiệt đới 67. water level (np) /ˈwɔːtə/ /ˈlevᵊl/ mực nước 3. WORD FORMATION No. Word Part of speech Pronunciation Meaning 68. nature (n) /ˈneɪʧə/ tự nhiờn, thiờn nhiờn 69. natural (adj) /ˈnổʧᵊrᵊl/ (thuộc) tự nhiờn, (thuộc) thiờn nhiờn 70. naturally (adv) /ˈnổʧrəli/ (thuộc) tự nhiờn, (thuộc) thiờn nhiờn 71. restore (v) /rɪsˈtɔː/ khụi phục 72. restoration (n) /ˌrestəˈreɪʃᵊn/ sự phục hồi 73. conserve (v) /kənˈsɜːv/ bảo tồn 74. conservation (n) /ˌkɒnsəˈveɪʃᵊn/ sự bảo tồn 75. disappear (v) /ˌdɪsəˈpɪə/ biến mất 76. disappearance (n) /ˌdɪsəˈpɪərᵊns/ sự biến mất 77. destroy (v) /dɪˈstrɔɪ/ phỏ huỷ 78. destruction (n) /dɪsˈtrʌkʃᵊn/ sự phỏ huỷ 79. danger (n) /ˈdeɪnʤə/ sự nguy hiểm 80. endangered (adj) /ɪnˈdeɪnʤəd/ bị đe dọa 81. ecology (n) /ɪˈkɒləʤi/ sinh thỏi học 82. ecological (adj) /ˌiːkəˈlɒʤɪkᵊl/ thuộc sinh thỏi học 2 Task 2. Find the word that differs from the other three in the position of stress in each of the following questions. 1. A. flora B. fauna C. destroy D. delta 2. A. resource B. native C. restore D. declare 3. A. provide B. reserve C. mammal D. marine 4. A. habitat B. natural C. scenery D. overuse 5. A. survival B. continent C. pangolin D. essential 6. A. endangered B. snorkeling C. cruelty D. waterway 7. A. freshwater B. located C. tropical D. national 8. A. alternative B. expectancy C. biological D. diversity 9. A. restoration B. ecological C. conservation D. fascinating 10. A. material B. ecosystem C. organism D. security II. VOCABULARY Task 1. Write the name under each picture. pangolin fishing cat great spotted eagle koala mangrove forest coral reef 1. __________________ 2. __________________ 3. __________________ 4. __________________ 5. __________________ 6. __________________ Task 2. Match the words/ phrases on the left with their meanings on the right. 1. mammal a. thick forest that grows in hot parts of the world 2. flora b. any animal that feeds its young on milk 3. fauna c. the protection of plants and animals, natural areas, etc. from the damage 4. biodiversity d. all the plants of a particular place or from a particular period 5. habitat e. a series of living things that are connected because each group of things eats the group below it in the series 6. ecosystem f. all the animals that live wild in a particular area 7. conservation g. the number and types of plants and animals that exist in a particular area or in the world generally 8. species h. the natural environment in which an animal or plant usually lives 9. food chain i. all the living things in an area and the way they affect each other and the environment 10. tropical forest j. a set of animals or plants which have similar characteristics to each other 4 6. To deal with climate change, it’s important to invest in alternative / ideal energy sources and reduce our reliance on carbon footprint / fossil fuels. 7. Snorkelling / Oil drilling in the Great Barrier Reef is a fascinating way to explore the marine ecosystem. 8. The overuse / launch of a new environmental law aims to promote the sustainability of natural resources / forest fire. 9. Living / Non-living things like rocks, water and soil playa role in shaping the landscape within an ecosystem. 10. Improved living conditions have led to an increase in life expectancy / wetlands in many parts of the world. III. GRAMMAR Task 1. Use the words in the box to make compound nouns, then match them to the suitable definitions below. wild water bird scuba life over way diving watching wet 1. A path or route for the flow of water, such as a river or canal. ___________________ 2. Animals that live independently of people, in natural conditions. ___________________ 3. A large area of land covered with swamp or marsh. ___________________ 4. The fact that something is used too often or too much, often leading to harm. ___________________ 5. The activity of observing birds in their natural environment. ___________________ 6. The sport of swimming underwater with special breathing equipment. ___________________ Task 2. Choose the correct word to make compound nouns that match their definitions. 1. Food system / chain: The order in which animals eat plants and each other in nature 2. Green / Blue job: A type of work that helps the environment, like recycling or planting trees 3. Forest burn / fire: A burning in an area of land with many trees, that is difficult to control 4. Mangrove / green forest: A kind of forest near the ocean with trees that grow in salty water 5. Rawing / Raw material: Anything like wood, oil or cotton in its natural condition before used to make other things 6. National garden / park: An area that is protected by the government because of its natural beauty and importance to history 7. Fishing / Fish cat: A kind of wild cat that likes to catch fish to eat 8. Coral rock / reef: An area of coral, the top of which can sometimes be seen just above the sea 9. No-take / No-get zone: A place where people can’t fish or hunt, so the animals and plants are protected 10. Non-living / life: Something that isn’t alive, like rocks or water. Task 3. Match a word on the left with a word on the right to make compound nouns, then fill in each blank with one suitable compound noun. carbon expectancy food forest(s) fossil reserve(s) marine drilling water fuel(s) life level tropical drilling natural species endangered security oil footprint 6 Task 2. Read the passage and decide whether the following statements are true (T), false (F) or not given (NG). An ecosystem is a geographic area where plants, animals, and other organisms, as well as weather and landscape, work together to form life. Ecosystems contain living parts, as well as non living parts. Living parts include plants, animals, and other organisms. Nonliving parts include rocks, temperature, and humidity. Every factor in an ecosystem depends on every other factor, either directly or indirectly. A change in the temperature of an ecosystem will often affect what plants will grow there, for instance. Animals that depend on plants for food and shelter will have to adapt to the changes, move to another ecosystem. The whole surface of Earth is a series of connected ecosystems. Ecosystems are often connected in a larger biome. Biomes are large sections of land, sea, or atmosphere. Forests, ponds and reefs are all types of biomes, for example. They’re organised very generally, based on the types of plants and animals that live in them, within each forest, each pond or each reef, you’ll find many different ecosystems. The biome of the Sahara Desert, for instance, includes a wide variety of ecosystems. The Sahara has oasis ecosystems which have palm trees and animals such as crocodiles, and dune ecosystems, which have animals such as snakes or scorpions. For thousands of years, people have interacted with ecosystems. As human populations have grown, however, people have overtaken many ecosystems and done harm to them. For example, human activity threatens all rain forest ecosystems in the Amazon. Thousands of acres of land are cleared for farmland, housing, and industry. Cutting down trees to make room for crops such as soy and corn benefits many poor farmers. However, the destruction of rain forest ecosystems has its costs. Many modern medicines have been developed from rainforest plants. Many scientists worry that destroying the rainforest ecosystem may prevent more medicines from being developed. Ecosystems can recover from destruction, however. Individual people, cultures, and governments are working to preserve ecosystems that are important to them. Adapted from https://education.nationalgeographic.org/resource/ecosystem/ ___________ 1. Living things include plants and rocks while non-living things include animals and temperature. ___________ 2. Factors in an ecosystem have effects on each other. ___________ 3. Biomes, which are sections of land, sea, or atmosphere, are larger than ecosystems. ___________ 4. Biomes are organised based on the types of plants and animals found in them. ___________ 5. The Sahara Desert biome contains oasis ecosystems with palm trees and snakes. ___________ 6. Cutting down trees for farmland in the rainforest benefits rich farmers. ___________ 7. Human activity poses a threat to rainforest ecosystems in the Amazon. ___________ 8. Rainforest plants have contributed to the development of modern medicines. ___________ 9. Damaging rainforest ecosystems has no negative consequences. ___________ 10. It is challenging for people and governments to recover ecosystems from damage. Task 3. Read the following passage and choose the correct answer to each of the following questions. Extinction is part of life on Earth. Through much of our planet’s history, species have been forming, evolving and eventually disappearing. Today, however, human activities have dramatically sped up the process. The Earth is losing animals, birds, and other living things so fast. There are many different views about why protecting it is important. Conservation biology is a scientific field with a mission: protecting and restoring biodiversity around the world. Michael Soulộ, one of the field’s founders, argued that biological diversity is good and should be conserved because it has intrinsic value. He also proposed that conservation biologists should act to save biodiversity even if sound science isn’t available to inform decisions. 8 C. Spending time in nature has negative impacts on human health. D. The loss of biodiversity can make ecosystems become stronger. 10. Which of the following is NOT true according to the passage? A. The value of the world’s ecosystems was greater than that of financial markets in 1997. B. Conserving Earth’s ecosystems and living creatures is essential for the benefits of all. C. Nature’s nonmonetary value for human health includes reducing stress and anxiety. D. Human activities have slowed down the process of species extinction on Earth. V. WRITING Task 1. Write meaningful sentences based on the given clues (form of the verb can be changed if necessary) 1. The Great Barrier Reef / home / variety / marine creatures. _____________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Sunda pangolins / endangered mammals / that / native / Southeast Asia. _____________________________________________________________________________________ 3. If / we / not / take action / protect / our forests, / we / may / run out / valuable resources. _____________________________________________________________________________________ 4. Scuba diving / allow / us / explore / fascinating / underwater ecosystems / coral reefs. _____________________________________________________________________________________ 5. forests / which / located / coastal regions / provide / protection / storms. _____________________________________________________________________________________ Task 2. Rewrite each sentence using the given word in brackets as long as its meaning stays the same as the original one. 1. The rise in green jobs has positive effects on the conservation of ecosystems. (BENEFICIAL) -> The rise ___________________________________________________________________________ 2. The destruction of the rainforest can badly affect the survival of many species. (THREATEN) -> The destruction _____________________________________________________________________ 3. If we continue to use our natural resources too much, we will cause loss of biodiversity. (OVERUSE) -> If we ______________________________________________________________________________ 4. Both individuals and governments should take responsibility for protecting the environment. (RESPONSIBLE) -> Both ______________________________________________________________________________ 5. Conservation organisations are of great importance to protect rare species from hunting. (ROLE) -> Conservation organisations ____________________________________________________________ Task 3. Write an essay (180-200 words) about the reasons why we should protect endangered species based on the following ideas ■ support people’s life ■ maintain biodiversity ■ provide health and cultural benefits _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 10
File đính kèm:
 bai_tap_bo_tro_tieng_anh_lop_11_global_success_unit_10_the_e.doc
bai_tap_bo_tro_tieng_anh_lop_11_global_success_unit_10_the_e.doc GS11_L_Unit 10 Task 1.mp3
GS11_L_Unit 10 Task 1.mp3 GS11_L_Unit 10 Task 2.mp3
GS11_L_Unit 10 Task 2.mp3 GS11_S_Unit 10 Task 1.mp3
GS11_S_Unit 10 Task 1.mp3 GS11_S_Unit 10 Task 2.mp3
GS11_S_Unit 10 Task 2.mp3 UNIT 10 - GV.doc
UNIT 10 - GV.doc

