Bài tập bổ trợ từ vựng và ngữ pháp Tiếng Anh Lớp 12 Global Success - Unit 4: Urbanisation (Có đáp án)
Bạn đang xem tài liệu "Bài tập bổ trợ từ vựng và ngữ pháp Tiếng Anh Lớp 12 Global Success - Unit 4: Urbanisation (Có đáp án)", để tải tài liệu gốc về máy hãy click vào nút Download ở trên.
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Bài tập bổ trợ từ vựng và ngữ pháp Tiếng Anh Lớp 12 Global Success - Unit 4: Urbanisation (Có đáp án)
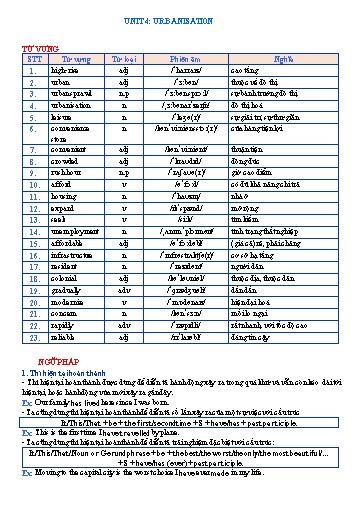
2. Cấu trúc so sánh 2.1. So sánh càng ngày càng Tính từ/trạng từ ngắn Tính từ/trạng từ dài Housing prices are getting higher and higher. Hanoi is becoming more and more polluted. 2.2. So sánh càng càng The + so sánh hơn + S + V, the + so sánh hơn + S + V. Ex: The bigger the city gets, the more crowded it becomes. PRACTICE Mark the letter A, B, C, or D to indicate the word whose underlined part differs from the other three in pronunciation in each of the following questions. Question 1. A. concern B. affordable C. convenience D. colonial Question 2. A. high-rise B. modernise C. housing D. sprawl Mark the letter A, B, C, or D to indicate the word that differs from the other three in the position of the primary stress in each of the following questions. Question 3. A. afford B. housing C. leisure D. urban Question 4. A. convenient B. employment C. expansion D. resident Mark the letter A, B, C, or D to indicate the correct answer to each of the following questions. Question 5. The city’s needs upgrading to meet the demands from its citizens. A. leisure B. convenience C. infrastructure D. unemployment Question 6. Youth crime in the inner city has increased in recent months, requiring tightened security. A. reliably B. affordably C. conveniently D. rapidly Question 7. Air pollution and traffic congestion are two major among city dwellers. A. concerns B. residents C. unemployment D. Infrastructure Question 8. The urban can threaten the unique charm of the countryside. A. unemployment B. housing C. leisure D. sprawl Question 9. Traffic in the is a nightmare for commuters. A. resident B. rush hour C. urbanisation D. concern Question 10. Many fresh graduates are struggling to a nine-to-five job. A. expand B. seek C. afford D. modernise Question 11. The municipal authority is implementing new policies to address affordable shortages. A. housing B. resident C. concern D. infrastructure Question 12. This is the first time Henry Ho Chi Minh’s Mausoleum. A. visited B. visits C. has visited D. had visited Question 13. The well is getting polluted, forcing villagers to seek alternative clean water sources. A. much and more B. much and much C. most and most D. more and more Question 14. The higher property prices are, city dwellers can afford. A. the fewest B. fewer than C. the fewer D. the fewer than (24) , urbanisation has created new problems. As more people come to seek better job opportunities, the city is getting more and more crowded. This has (25) to more traffic jams and higher unemployment rates. Air pollution is also causing concern among city residents. (Adapted from Global Success) Question 21. A. afforded B. expanded C. modernised D. concerned Question 22. A. housing B. concerns C. residents D. convenience Question 23. A. expected B. affected C. imagined D. structured Question 24. A. Therefore B. In addition C. However D. For example Question 25. A. related B. resulted C. led D. complied Read the following passage and mark the letter A, B, C, or D to indicate the correct answer to each of the questions from 26 to 30. Urbanisation in Malaysia started in the early 1970s. At that time, only around 26 per cent of the population lived in urban areas. After a period of rapid growth, the urban and rural populations were almost equal in the early 1990s. Since then, the urbanisation rate has continued to increase gradually. The urban population, for example, rose from 66 per cent in 2004 to 74 per cent in 2014. At present, Malaysia is known as one of the most urbanised countries in East Asia. It is also one of the most rapidly urbanised regions around the world. According to the latest statistics, over 77 per cent of Malaysia's total population now live in urban areas and cities. Australia is an interesting example of early urbanisation, which started at the end of the 19th century. At that time, over 60 per cent of the population lived in urban areas. Since then, it has maintained a gradual growth. This was also due to the country's immigration policy, which encouraged people to settle in its coastal, urban areas. Australia is now one of the most urbanised countries in the world, with almost 90 per cent of the population living in urban areas. The two largest cities of Australia, Sydney and Melbourne, are home to over 40 per cent of the country's population. (Adapted from Global Success) Question 26. What does the passage mainly discuss? A. Challenges facing urbanised Malaysia and Australia B. The brief history of Malaysia and Australia C. Urbanisation in Malaysia and Australia D. Housing problems in Malaysia and Australia Question 27. The word rose in paragraph 1 is opposite in meaning to _ . A. increased B. developed C. evolved D. declined Question 28. According to paragraph 1, Malaysia . A. is the most urbanised country in East Asia B. has only 26% of its population living in urban areas C. has witnessed a decrease in the urbanisation rate D. is one of the most rapidly urbanised countries in the world Question 29. The word its in paragraph 2 refers to . A. immigration policy B. a gradual growth C. early urbanisation D. Australia Question 30. Which of the following is NOT true according to paragraph 2? A. Australia’s immigration policy contributed to the growth of its urban population. B. Urbanisation in Australia started at the end of the 19th century. C. There are nearly 60 per cent of people living in urban areas in Australia. D. Sydney and Melbourne are the two most crowded cities in Australia.
File đính kèm:
 bai_tap_bo_tro_tu_vung_va_ngu_phap_tieng_anh_lop_12_global_s.docx
bai_tap_bo_tro_tu_vung_va_ngu_phap_tieng_anh_lop_12_global_s.docx UNIT 4- GV.docx
UNIT 4- GV.docx UNIT 4- GV.pdf
UNIT 4- GV.pdf UNIT 4- HS.pdf
UNIT 4- HS.pdf

