Bài tập Tiếng Anh Lớp 11 Global Success - Unit 3: Cities of the future (Có file nghe và đáp án)
Bạn đang xem tài liệu "Bài tập Tiếng Anh Lớp 11 Global Success - Unit 3: Cities of the future (Có file nghe và đáp án)", để tải tài liệu gốc về máy hãy click vào nút Download ở trên.
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Bài tập Tiếng Anh Lớp 11 Global Success - Unit 3: Cities of the future (Có file nghe và đáp án)
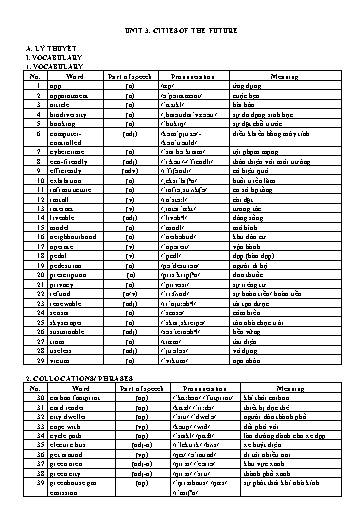
40. high-rise building (adj-n) /ˈhaɪraɪz/ /ˈbɪldɪŋ/ nhà cao tầng 41. household chore (np) /ˈhaʊshəʊld/ /ʧɔː/ việc nhà 42. housing problem (np) /ˈhaʊzɪŋ/ /ˈprɒbləm/ vấn đề nhà ở 43. make up of (vp) /meɪk/ /ʌp/ /ɒv/ tạo nờn 44. medical check-up (adj-n) /ˈmɛdɪkəl/ /ʧɛk/-/ʌp/ kiểm tra sức khoẻ 45. one-way trip (adj-n) /wʌn/-/weɪ/ /trɪp/ chuyến đi một chiều 46. parking space (np) /ˈpɑːkɪŋ/ /speɪs/ chỗ đậu xe 47. pedestrian zone (np) /pəˈdestriən/ /zəʊn/ khu vực dành cho người đi bộ 48. private vehicle (adj-n) /ˈpraɪvɪt/ /ˈviːɪkl/ phương tiện cỏ nhõn 49. public transport (np) /ˈpʌblɪk/ /ˈtrổnspɔːt/ phương tiện giao thụng cụng cộng 50. roof garden (np) /ruːf/ /ˈɡɑːdn/ vườn trờn sõn thượng 51. rooftop farming (np) /ˈruːfˌtɒp/ /ˈfɑːmɪŋ/ canh tỏc trờn sõn thượng 52. route (np) /ruːt/ sự gợi ý tuyến đường recommendation /ˌrɛkəmɛnˈdeɪʃᵊn/ 53. sense of (np) /sɛns/ /ɒv/ ý thức cộng đồng community /kəˈmjuːnəti/ 54. smart city (adj-n) /smɑːt/ /ˈsɪti/ thành phố thụng minh 55. smart sensor (adj-n) /smɑːt/ /ˈsɛnsə/ cảm biến thụng minh 56. street light (np) /striːt/ /laɪt/ đốn đường 57. urban area (adj-n) /ˈɜːbən/ /ˈeərɪə/ khu vực đụ thị 58. urban centre (adj-n) /ˈɜːbən/ /ˈsɛntə/ trung tõm đụ thị 59. underground (np) /ˈʌndəɡraʊnd/ canh tỏc dưới lũng đất farming /ˈfɑːmɪŋ/ 60. work out (vp) /wɜːk/ /aʊt/ tớnh toỏn 3. WORD FORMATION No. Word Part of speech Pronunciation Meaning 61. environment (n) /ɪnˈvaɪərənmənt/ mụi trường 62. environmental (adj) /ɪnˌvaɪərənˈmɛntl/ (thuộc) mụi trường 63. interact (v) /ˌɪntərˈổkt/ tương tỏc 64. interaction (n) /ˌɪntərˈổkʃᵊn/ sự tương tỏc 65. recommend (v) /ˌrɛkəˈmɛnd/ gợi ý, đề nghị 66. recommendation (n) /ˌrɛkəmɛnˈdeɪʃᵊn/ sự đề nghị, sự gợi ý 67. renew (v) /rɪˈnjuː/ làm mới 68. renewable (adj) /rɪˈnjuːəbᵊl/ tỏi tạo được 69. sense (n) /sɛns/ cảm giỏc 70. sensor (n) /ˈsɛnsə/ mỏy cảm biến II. PRONUNCIATION Cỏch nối phụ õm cuối của một từ với nguyờn õm đầu của một từ khỏc khi núi - Để núi tiếng Anh một cỏch tự nhiờn, chỳng ta sẽ khụng dừng ở giữa phần lớn cỏc từ. Thay vào đú, chỳng ta sẽ nối õm từ cuối từ này sang đầu từ khỏc để để giỳp cõu văn dễ núi và liền mạch hơn. - Việc nối phụ õm với nguyờn õm giữa cỏc từ rất phổ biến trong tiếng Anh và đặc biệt là khi nối phụ õm cuối của một từ với nguyờn õm đầu của một từ khỏc. Vớ dụ: 1. Cities∪of the future will be more∪exciting. /’sɪtiz/∪/ɒv/ /ðə/ /’fju:tʃə/ /wɪl/ /bi:/ /mɔ:r/∪/ɪk’saɪtɪŋ/. 2. The new high-rise building is∪in the west ∪of the city. /ðə/ /nju:/ /’haɪraɪz/ /’bɪldɪŋ/ /ɪz/∪/ɪn/ /ðə/ /wɛst/∪/ɒv/ /ðə/ /’sɪti/. Task 2. Find the word that differs from the other three in the position of stress in each of the following questions. 1. A. city B. area C. public D. install 2. A. private B. transport C. sustainable D. vehicle 3. A. biodiversity B. dweller C. sensor D. infrastructure 4. A. problem B. carbon C. footprint D. computer 5. A. building B. controlled C. centre D. urban 6. A. emission B. farming C. underground D. skyscraper 7. A. liveable B. privacy C. pedestrian D. cybercrime 8. A. interact B. article C. neighbourhood D. operate 9. A. pedal B. community C. reader D. greenhouse 10. A. booking B. rooftop C. future D. prescription II. VOCABULARY Task 1. Match the words or phrases with the pictures. 1. roof garden a. 2. skyscraper b. 3. pedestrian zone c. 4. tram d. 5. cycle path e. Task 2. Match the words on the left with their meanings on the right. 1. public transport ______ a. a person who lives in a city 2. carbon footprint ______ b. the amount of greenhouse gases, like carbon dioxide, produced by our activities 3. city dweller ______ c. gas, especially carbon dioxide, that prevents heat from the earth escaping into space 4. urban centre ______ d. a system of transport that is available for use by the general public, including services such as buses, trains, trams, and subways. 5. greenhouse gas ______ e. the middle part of a city/town 2. The route recommendation system in the city uses artificial intelligence algorithms and real-time traffic data to reduce travel time. A. suggestion B. denial C. refusal D. opposition 3. The customer care policies allow residents and businesses to request and receive refunds for services easily. A. penalties B. credits C. fines D. compensations 4. The city operates efficiently through a network of public services and innovative technologies. A. releases B. overlooks C. functions D. neglects 5. Future cities will need to implement innovative solutions to cope with the challenges of rapid urbanization and population growth. A. deal with B. get rid of C. run for D. do away with Task 6. Complete the sentences using the correct form of the word in brackets. 1. Doctors are responsible for giving out ____________________, so people can get the right medicines and treatments for their health problems. (PRESCRIBE) 2. The city uses smart technology and sustainable practices to save energy and manage resources ____________________. (EFFICIENCY) 3. The city focuses on creating a ____________________ environment, by creating more green spaces and reliable infrastructure. (LIFE) 4. With a more efficient public transportation system, the city encourages more residents to use ____________________ vehicles. (PRIVACY) 5. The city implements convenient card ____________________ systems across public transportation and key facilities. (READ) 6. In future cities, ____________________ will be widely used to gather real-time data and improve the efficiency of various urban systems and services. (SENSE) 7. The city implements a user-friendly ____________________ platform allowing residents and tourists to reserve various services easily. (BOOK) 8. ____________________ energy sources, such as solar and wind power, are crucial for reducing the use of fossil fuels. (RENEW) 9. The government plays an important role in ____________________ protection by promoting green spaces. (ENVIRONMENT) 10. Smart cities create environments where citizens can easily ____________________ with various urban systems, such as transportation and public services. (INTERACTION) Task 7. Choose the correct words to complete the sentences. 1. Cities worldwide are adopting eco-friendly / useless ideas such as renewable energy, green transportation. 2. The city implemented various measures to reduce the number of crime victims / appointments in the community. 3. The city offers various transportation options, making it easy for residents and visitors to work out / get around and explore all its attractions. 4. I spent my Saturday morning doing household chores / models like washing the dishes, cleaning the floors, and folding clothes. 5. The city recently introduced renewable / electric buses as a sustainable and eco- friendly mode of public transportation. III. GRAMMAR Task 1. Choose the appropriate verb form to complete the sentences. 1. Smart cities are becoming / become more efficient and connected. 2. Smart cities look / are looking modern with smart infrastructure and digital technologies everywhere. Growing numbers of active ageing seniors are “connected” everyday (3) ______ mobile phones to interact with smart city services. (4) ______ have wearable devices like smart watches (5) ______ help monitor and manage their health and physical activity. These personal devices can also be used to better connect older adults to public data about urban environments. (6) ______, imagine an age-friendly smart city “layer” linked (7) ______ a smart watch, to highlight facilities such as public toilets, water fountains and shaded rest stops along exercise routes. Access Map Seattle is an example of an age-friendly, (8) ______, smart city map that shows the steepness of pedestrian footpaths and raised kerbs. The National Public Toilet Map, (9) ______ by the Australian Department of Health and Ageing, and Barcelona’s smart app city are (10) ______ other mobile apps integrating city services and urban plans. Source: https://theconversation.com/this-is-how-we-create-the-age-friendly-smart-city-152973 1. A. knowledge B. access C. tools D. skills 2. A. motivated B. hindered C. asked D. demanded 3. A. use B. used C. to use D. using 4. A. Many B. Few C. Little D. Much 5. A. who B. why C. that D. where 6. A. Therefore B. Nevertheless C. For example D. In addition 7. A. from B. to C. of D. in 8. A. interact B. interaction C. interactively D. interactive 9. A. create B. to create C. created D. creating 10. A. between B. among C. of D. from Task 2. Read the following passage and choose the correct answer to each of the questions. Cyber-security and technology ethics are important topics. Smart cities represent a complex new field for governments, citizens, designers and security experts to navigate. The privatisation of civic space and public services is a hidden cost too. The complexity of smart city systems and their need for ongoing maintenance could lead to long-term reliance on a tech company to deliver public services. Many argue that, by improving data collection and monitoring and allowing for real-time responses, smart systems will lead to better environmental outcomes. For instance, waste bins that alert city managers when they need collecting, or that prompt recycling through tax credits, and street lamps that track movement and adjust lighting levels have the potential to reduce energy use. But this runs contrary to studies that show more information and communication technology actually leads to higher energy use. At best, smart cities may end up a zero-sum game in terms of sustainability because their “positive and negative impacts tend to cancel each other out”. And then there’s the less-talked-about issue of e-waste, which is a huge global challenge. Adding computers to objects could create what one writer has termed a new “internet of trash” - products designed to be thrown away as soon as their batteries run down. As cities become smart they need more and more objects - street lamps, public furniture, signboards - to integrate sensors, screens, batteries and processors. Objects in our cities are usually built with durable materials, which means they can be used for decades. Computer processors and software systems, on the other hand, are short-lived and may need upgrading every few years. Adding technology to products that didn’t have this in the past effectively shortens their life-span and makes servicing, warranties and support contracts more complex and unreliable. One outcome could be a landscape of smart junk - public infrastructure that has stopped working, or that needs ongoing maintenance and upgrades. Source: https://theconversation.com/technology-is-making-cities-smart-but-its-also-costing-the- environment-99296 1. Which of the following will be the best title for the passage? A. Downsides of Smart cities B. Technology in Smart cities _____________________________________________________________________________________ 2. people / large / More / from / the / cities. / centre / moving / urban / of / away / are (12 words) _____________________________________________________________________________________ 3. cities / people’s / on / to / Smart / are / improve / built / lives. / technologies (10 words) _____________________________________________________________________________________ 4. app / make / allows / The / a / space / payment. / and / parking / a / mobile / you / book / to (14 words) _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 5. worried / because / become / information / protected. / people / personal / their / not / be / might (11 words) _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Task 2. Mark the letter A, B, C or D to indicate the sentence that is closest in meaning to each of the given sentences. 1. Sensors and cameras collect information about people and their activities. A. Sensors and cameras delete information about people and their activities. B. Information about people and their activities are collected by sensors and cameras. C. Information about people and their activities collected by sensors and cameras. D. Sensors and cameras ignore information about people and their activities. 2. Without training, people will not know how to use the technologies in the smart city. A. People will easily learn how to use the technologies in the smart city without training. B. People may struggle to use the technologies in the smart city if they receive training. C. People will know how to use the technologies in the smart city even without training. D. People will lack the knowledge to use the technologies in the smart city without training. 3. The project aims to improve the city’s old infrastructure by creating more pedestrian zones and cycle paths. A. The project intends to deteriorate the city’s existing infrastructure by reducing pedestrian zones and cycle paths. B. The project aims to prioritise the city’s old infrastructure by disregarding the need for pedestrian zones and cycle paths. C. The purpose of the project is to enhance the city’s outdated infrastructure by constructing additional areas for pedestrians and cyclists. D. The purpose of the project is to prioritise the city’s old infrastructure by neglecting the creation of pedestrian zones and cycle paths. 4. According to some experts, the negative impacts on the environment of smart cities are fewer than normal cities. A. According to some experts, smart cities have more negative impacts on the environment than regular cities. B. According to some experts, smart cities have fewer negative environmental influences than regular cities. C. According to some experts, the smart city has no negative impacts on the environment unlike normal cities. D. According to some experts, the smart city has equal negative impacts on the environment as normal cities. 5. The apartment in the urban centre was expensive, so my parents could not afford it. A. The apartment in the urban centre was affordable, so my parents decided to buy it. B. The apartment in the urban centre was cheap, and my parents bought it. C. The apartment in the urban centre was too expensive for my parents to buy. D. The apartment in the urban centre was reasonably priced, so my parents considered buying it.
File đính kèm:
 bai_tap_tieng_anh_lop_11_global_success_unit_3_cities_of_the.doc
bai_tap_tieng_anh_lop_11_global_success_unit_3_cities_of_the.doc 3. GS11_L_Unit3 Task1.mp3
3. GS11_L_Unit3 Task1.mp3 3. GS11_L_Unit3 Task2.mp3
3. GS11_L_Unit3 Task2.mp3 3. GS11_S_Unit3 Task1.mp3
3. GS11_S_Unit3 Task1.mp3 3. GS11_S_Unit3 Task2.mp3
3. GS11_S_Unit3 Task2.mp3 UNIT 3. CITIES OF THE FUTURE - KEY.doc
UNIT 3. CITIES OF THE FUTURE - KEY.doc

