Bài tập Tiếng Anh Lớp 11 Global Success - Unit 5: Global warming (Có file nghe và đáp án)
Bạn đang xem tài liệu "Bài tập Tiếng Anh Lớp 11 Global Success - Unit 5: Global warming (Có file nghe và đáp án)", để tải tài liệu gốc về máy hãy click vào nút Download ở trên.
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Bài tập Tiếng Anh Lớp 11 Global Success - Unit 5: Global warming (Có file nghe và đáp án)
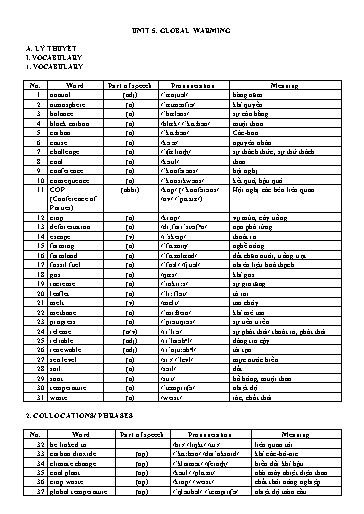
38. global warming (np) /ˈɡləʊbəl/ /ˈwɔːmɪŋ/ sự nĩng lên tồn cầu 39. greenhouse effect (np) /ˈɡriːnhaʊs/ /ɪˈfɛkt/ hiệu ứng nhà kính 40. heat stress (np) /hiːt/ /strɛs/ ứng suất nhiệt 41. heat-trapping (adj-n) /hiːt/-/ˈtrỉpɪŋ/ chất gây ơ nhiễm giữ nhiệt pollutant /pəˈluːtənt/ 42. human activity (np) /ˈhjuːmən/ /ỉkˈtɪvəti/ hoạt động của con người 43. landfill waste (np) /ˈlỉndfɪl/ /weɪst/ chất thải ở bãi rác 44. natural gas (np) /ˈnỉʧrəl/ /ɡỉs/ khí tự nhiên 45. open fire (np) /ˈəʊpən/ /ˈfaɪə/ ngọn lửa trần 46. polar ice cap (np) /ˈpəʊlər/ /aɪs/ /ˈkỉp/ chỏm băng vùng cực 47. renewable energy (adj-n) /rɪˈnjuːəbᵊl/ /ˈɛnəʤi/ năng lượng tái tạo 48. responsible for (adj-pre) /rɪsˈpɒnsəbᵊl/ /fɔː/ chịu trách nhiệm cho 49. rising sea level (adj-n) /ˈraɪzɪŋ/ /siː/ /ˈlɛvl/ mực nước biển dâng cao 50. run out (vp) /rʌn/ /aʊt/ hết, cạn kiệt 51. suffer from (vp) /ˈsʌfə/ /frɒm/ chịu đựng 52. United Nations (np) /jʊˈnaɪtɪd/ /ˈneɪʃᵊnz/ Liên Hợp Quốc 3. WORD FORMATION No. Word Part of speech Pronunciation Meaning 53. emit (v) /iˈmɪt/ phát thải 54. emission (n) /ɪˈmɪʃᵊn/ sự phát thải, khí thải 55. environment (n) /ɪnˈvaɪərənmənt/ mơi trường 56. environmental (adj) /ɪnˌvaɪ.rənˈmen.təl/ thuộc về mơi trường 57. pollute (v) /pəˈluːt/ làm ơ nhiễm, gây ơ nhiễm 58. pollutant (n) /pəˈluːtənt/ chất gây ơ nhiễm 59. pollution (n) /pəˈluː.ʃən/ sự ơ nhiễm II. PRONUNCIATION Trọng âm câu và âm điệu Trong một câu, trọng âm của câu thường rơi vào những từ chứa thơng tin quan trọng. Các từ được nhấn mạnh bao gồm danh từ, động từ, tính từ và trạng từ. Cịn những từ chức năng như đại từ, giới từ, lượng từ, mạo từ, liên từ thì sẽ khơng được nhấn mạnh. Sự phối hợp nhuần nhuyễn giữa các âm tiết được nhấn mạnh và khơng được nhấn mạnh tạo thành âm điệu cho câu, giúp câu nĩi trở nên tự nhiên và trơi chảy hơn. Ví dụ: 1. She bought a new car. 2. The kids are at the park. 3. She is going to study tonight. Trong các câu bên trên, những từ được gạch chân là những từ mang thơng tin nên thường được nhấn mạnh. III. GRAMMAR Mệnh đề hiện tại phân từ/quá khứ phân từ 1. MỆNH ĐỀ HIỆN TẠI PHÂN TỪ - Định nghĩa: Hiện tại phân từ là động từ cĩ đuơi -ing và được dùng với nghĩa chủ động. Hiện tại phân từ được dùng để tạo mệnh đề hiện tại phân từ khi phân từ và động từ trong mệnh đề chính cĩ cùng chủ ngữ và hành động được thực hiện bởi cùng một người hoặc vật. - Cách dùng: Mệnh đề hiện tại phân từ được dùng trong các trường hợp sau: coal plant open fire black carbon polar ice caps landfill waste methane deforestation fossil fuels 1. ________________ 5. ________________ 2. ________________ 6. ________________ 3. ________________ 7. ________________ 4. ________________ 8. ________________ Task 2. Complete the following sentences with suitable words or phrases from Task 1. Make any changes if necessary. 1. The excess amount of waste in landfills can release ___________________, a greenhouse gas. 2. Burning ___________________ like oil, coal, and natural gas releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, contributing to global warming. 3. The emission of ___________________ from vehicles and industries has negative effects on air quality and our health. 4. ________________ release smoke and harmful gases, so many countries are trying to replace them with cleaner energy sources. 5. People in some parts of the world still cook their food over a (an) ___________________, which can produce smoke and pollution. 6. The amount of ___________________ can be reduced by recycling, reusing, and composting our everyday items. 7. The melting of the ___________________ is one of the causes of rising sea levels, which can be linked to global warming. 8. The ___________________ of the Amazon rainforest contributes to the loss of animal homes and valuable farmland. Task 3. Match the words or phrases on the left with their meanings on the right. 1. carbon dioxide a. refers to significant and long-term changes in the Earth’s weather patterns, including temperature, wind and so on. 1. The use of ____________________ sources, such as wind, solar and hydroelectric power is beneficial to tackle global warming. 2. ____________________ like deforestation and burning fossil fuels raise global temperatures. 3. The increasing amount of carbon dioxide in the ____________________ is a major contributor to global warming. 4. Global warming is the long-term increase in the Earth’s average temperature due to human activities and the release of ____________________ pollutants. 5. ____________________, resulting from higher temperatures, can negatively impact human health, agriculture, and wildlife. Task 7. Choose the correct answers to complete the sentences. 1. Burning fossil fuels like coal and natural gas can release / melt heat-trapping pollutants into the atmosphere. 2. Using renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, can help escape / decrease greenhouse gas emissions. 3. Healthy soot / soil is essential for promoting sustainable agriculture and maintaining a balanced ecosystem. 4. Soil degradation and waste of farmland are some of the causes / consequences of unsustainable farming practices. 5. Human activities, such as burning fossil fuel sand deforestation, are largely responsible / available for the greenhouse effect and climate change. 6. Reducing carbon dioxide emissions is a challenge / waste in tackling global warming and preventing further environmental damage. 7. Renewable energy is considered a reliable / negative and environmentally friendly alternative to fossil fuels. 8. Many regions around the world run out / suffer from the consequences of global warming, such as rising temperatures and extreme weather events. III. GRAMMAR Task 1. Mark the letter A, B, C or D to indicate the correct answer to each of the following questions. 1. _______ by human activities, global warming has become a major concern for scientists and policymakers. A. Causing B. Caused C. Cause D. Causes 2. The melting ice caps, _______ to rising sea levels, present a threat to coastal communities. A. link B. linking C. links D. linked 3. _______ crops in the changing climate conditions, farmers are often faced with many challenges. A. Growing B. Growth C. Grown D. Grow 4. Landfill waste, _______ overtime, can have a negative impact on the environment. A. is gathered B. gathering C. gathered D. gather 5. The leaflets _______ by environmental organisations aim to raise awareness of the dangers of deforestation. A. distribute B. distributed C. distributing D. are distributed Task 2. Choose the correct answers to complete the sentences. 1. Using / Used renewable energy sources, we can reduce our dependence on fossil fuels and decrease greenhouse gas emissions. 2. Melted / Melting at an alarming rate due to an increase in temperatures, polar ice caps are causing sea levels to rise. 3. Released / Releasing large amounts of carbon dioxide, coal plants contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions. 1. A. cause B. consequence C. contributor D. measure 2. A. to B. for C. with D. of 3. A. that B. then C. which D. where 4. A. therefore B. as C. but D. and 5. A. under B. for C. at D. in 6. A. favourable B. pleasant C. decent D. extreme 7. A. reduced B. reduction C. reducing D. reduce 8. A. less B. more C. much D. fewer 9. A. related B. compared C. connected D. regarded 10. A. restored B. restore C. restoration D. restoring Task 2. Read the following passage and choose the correct answer to each of the following questions. Global warming is the long-term warming of the planet’s overall temperature. Though this warming trend has been going on for a long time, its pace has significantly increased in the last hundred years due to the burning of fossil fuels. As the human population has increased, so has the volume of fossil fuels burned. Fossil fuels include coal, oil, and natural gas, and burning them causes what is known as the “greenhouse effect” in Earth’s atmosphere. The greenhouse effect is when the sun’s rays penetrate the atmosphere, but when that heat is reflected off the surface cannot escape back into space. Gases produced by the burning of fossil fuels prevent the heat from leaving the atmosphere. These greenhouse gases are carbon dioxide, chlorofluorocarbons, water vapour, methane, and nitrous oxide. The excess heat in the atmosphere has caused the average global temperature to rise overtime, otherwise known as global warming. Global warming has presented another issue called climate change. Sometimes these phrases are used interchangeably, however, they are different. Climate change refers to changes in weather patterns and growing seasons around the world. It also refers to sea level rise caused by the expansion of warmer seas and melting ice sheets and glaciers. Global warming causes climate change, which poses a serious threat to life on Earth in the forms of widespread flooding and extreme weather. Scientists continue to study global warming and its impact on Earth. Source: https://education.nationalgeographic.org/resource/global-warming/ 1. Which of the following can be the best title for the passage? A. A Brief Introduction to Global Warming B. The Effects of Global Warming on Earth’s Climate C. The Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming D. The Link between Fossil Fuels and Global Warming 2. According to paragraph 1, what has significantly led to the rising pace of global warming in the last hundred years? A. Increased population B. Burning of fossil fuels C. Natural disasters D. Solar activity 3. The word “penetrate” in paragraph 2 is closest in meaning to _______. A. break in B. move through C. come across D. go into 4. According to paragraph 2, how does the greenhouse effect work? A. It reflects the sun’s rays off the Earth’s surface. B. It causes the burning of fossil fuels. C. It prevents the heat from escaping the atmosphere. D. It increases the average global temperature. 5. According to paragraph 2, which gases are contributors to the greenhouse effect? A. oxygen and nitrous oxide B. carbon dioxide and methane C. hydrogen and water vapour D. nitrogen and chlorofluorocarbons 6. The word “interchangeably” in paragraph 3 is closest in meaning to _______. A. exclusively B. collectively C. replaceably D. irreplaceably V. WRITING Task 1. Reorder the given words and phrases to form meaningful sentences. 1. responsible / in / We / are / emissions. / greenhouse / for / the / increase / gas (10 words) _____________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Soot / affects / plants / is / pollutant / major / from / that / a / air / coal / quality. (12 words) _____________________________________________________________________________________ 3. rising / The / sea / linked / is / the / to / polar / melting / ice / level / of / caps. (13 words) _____________________________________________________________________________________ 4. a / balance / impact / Deforestation / the / significant / on / of / has / environment. / the (11 words) _____________________________________________________________________________________ 5. practices / impact / growth. / nutrients / the / Farming / of / can / soil / and / crop / balance (12 words) _____________________________________________________________________________________ Task 2. Rewrite the following sentences using present or past participle clauses based on the given words. 1. Many companies raise awareness of impacts of carbon emissions, so they promote the use of renewable energy resources. -> Raising ____________________________________________________________________________ 2. Open fires and burning fossil fuels release soot and black carbon, which have negative effects on air quality. -> Released ___________________________________________________________________________ 3. Deforestation reduces carbon absorption by trees so it affects the balance of the ecosystem badly. -> Reducing __________________________________________________________________________ 4. The destruction of coral reefs results from rising ocean temperatures, so it threatens ocean biodiversity. -> Resulting __________________________________________________________________________ 5. If the ozone layer is damaged badly, it will affect human health and ecosystems. -> Damaged __________________________________________________________________________ Task 3. Write a paragraph (120-150 words) about solutions to climate change. _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ VI. SPEAKING Task 1. Answer the following questions. 1. Do you care about global warming? _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Is this phenomenon affecting your life? _____________________________________________________________________________________
File đính kèm:
 bai_tap_tieng_anh_lop_11_global_success_unit_5_global_warmin.doc
bai_tap_tieng_anh_lop_11_global_success_unit_5_global_warmin.doc 5. GS11_L_Unit5 Task1.mp3
5. GS11_L_Unit5 Task1.mp3 5. GS11_L_Unit5 Task2.mp3
5. GS11_L_Unit5 Task2.mp3 5. GS11_S_Unit5 Task1.mp3
5. GS11_S_Unit5 Task1.mp3 5. GS11_S_Unit5 Task2.mp3
5. GS11_S_Unit5 Task2.mp3 UNIT 5. GLOBAL WARMING - KEY.doc
UNIT 5. GLOBAL WARMING - KEY.doc

