Bài tập Tiếng Anh Lớp 7 Global Success - Chương trình học kì 2 (Có file nghe)
Bạn đang xem 30 trang mẫu của tài liệu "Bài tập Tiếng Anh Lớp 7 Global Success - Chương trình học kì 2 (Có file nghe)", để tải tài liệu gốc về máy hãy click vào nút Download ở trên.
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Bài tập Tiếng Anh Lớp 7 Global Success - Chương trình học kì 2 (Có file nghe)
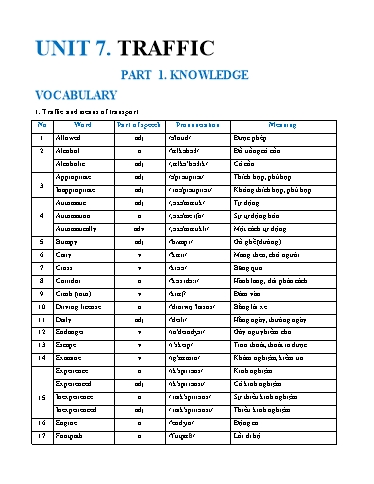
18 Fasten v /'fổsn/ Thắt, cài 19 Signal v / sɪgnəl / Tớn hiệu, xi nhan 20 Give a signal v /gɪv ə 'sɪgnəl/ Đưa tớn hiệu, xi nhan 21 Handlebars n /'hổndlbɑːz/ Ghi đụng xe đạp 22 Helmet n /'helmɪt/ Mũ bảo hiểm 23 Indicate v /'ɪndɪkeit/ Chỉ, xỏc định cỏi gỡ 24 Increase n, v /ɪn'kri:s/ Tăng, sự tăng lờn Install v /ɪ'stɔːl/ Lắp đặt, cài đặt 25 Installation n /.ɪnstə'leiʃn/ Sự lắp đặt, cài đặt 26 Junction n /'dʒʌŋkʃn/ Giao lộ, điểm giao nhau Lane n /lein/ Làn đường 27 Cycle lane n /'saikl lein/ Làn đường cho xe đạp Law n /lɔː/ Luật 28 Lawful adj /'lɔ:fl/ Hợp phỏp, tuõn theo luật unlawful adj /ʌn'lɔ:fl/ Bất hợp phỏp Legal adj /’li:gl/ Hợp phỏp legally adv /'li:gəlɪ/ Một cỏch hợp phỏp 29 Illegal adj /ɪ'li:gl/ Bất hợp phỏp Illeglly adv /ɪ'li:gəli/ Một cỏch bất họp phỏp Left-handed adj /.left 'hổndɪd/ Thuận tay trỏi 30 Right-handed adj /.rait'hổndɪd/ Thuận tay phải 31 Light-coloured adj /,lait 'kʌlərd/ Màu sỏng Means of /mi:nzəv 32 n Phương tiện giao thụng transport 'trổnspɔːrt/ 33 Mechanical fault n /mə'kổnɪkl fɔːlt/ Lỗi kĩ thuật Obey v /ə'bei/ Tuõn thủ 34 Obedient adj /ə'bi:diənt/ Biết nghe lời Obedience n /ə'bi:diəns/ Sự tuõn thủ /.əʊpən 35 Open-air market n Chợ trời 'eər 'mɑːrkɪt/ Prohibit v /prə'hɪbɪt/ Cấm 36 Prohibition n /.prəʊɪ'bɪʃn/ Sự cấm đoỏn 58 Warn (of) V /wɔːrn/ Cảnh bỏo (về) 59 Wave V /weiv/ vẫy, gọi 60 Watch out V /wɒtʃ aʊt/ Coi chừng, cẩn trọng 61 Zebra crossing n /'zi:brə 'krɔːsɪŋ/ Vạch sang đường 2. Traffic signs 1 ... ahead Cỏi gỡ ở phớa trước 2 Keep to the right / left Đi theo hướng bờn phải / trải 3 No cycling Khụng đạp xe 4 No parking Cấm đỗ xe 5 No right / left turn Cấm rẽ phải/ trỏi 6 Turn red / yellow / green Đốn chuyển màu đỏ / vàng /xanh 3. Collocations: Verb with means of transsport No. Word Part of speech Meaning 1 Board a coach / plane / train... Lờn xe khỏch, mỏy bay, tàu 2 a bus / taxi / train / ferry / Bat xe buýt, tắc xi, tàu, phà; Catch flight/ plane ... lờn mỏy bay 3 Drive a car/bus/taxi/coach... Lỏi xe ụ tỏ, xe buýt, tắc xi, xe khỏch 4 Fly a plane Lỏi mỏy bay 5 a bus / coach / train / bike / Lờn xe, tàu ... Get on motorbike... (phương tiện cụng cộng và thụ sơ) 6 a bus / coach / train / bike / Xuống xe / tàu... Get off motorbike... (phương tiện cụng cộng và thụ sơ) 7 Get in(to) a car/taxi Lờn xe (phương tiện cỏ nhõn, tư nhõn) 8 Get out (of) a car/taxi Xuống xe (phương tiện cỏ nhõn, tư nhõn) 9 Ride a bike / motorbike / tricycle Lỏi xe đạp, xe mỏy... 10 Sail (in/on) a boat / ship Chốo thuyền, tàu PART 2. PRACTICE LESSON 1. LISTENING Activity 1. Listen to the recording and tick the correct pictures. - Track 01 ___________________ and slow to travel on due to outdated design and an inappropriate traffic mix. In recent years, the construction of expressways have accelerated. Air (4) ___________________ is also important for long-distance travel. Metro (5) ___________________ are under construction in the two metropolises of Viet Nam, Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City. Activity 3. Listen to the recording and find one mistake in each sentence. - Track 03 1. Viet Nam is renowned for its bike culture. __________________________________________________________________________________ 2. In 2037, 79% of Vietnamese reported using a motorbike regularly. __________________________________________________________________________________ 3. With 45 million registered motorbikes on a 29 million population headcount, Viet Nam has one of the highest motorbike ownership rates worldwide. __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 4. Viet Nam is the 14th largest market for motorbike sales, after China, India, and Indonesia. __________________________________________________________________________________ 5. 87% of Japanese households own a motorbike, a number only surpassed by Thailand. __________________________________________________________________________________ Activity 4. Listen to the recording and reorder the sentences to make a paragraph. - Track 04 A. Australia is highly dependent on road transport. B. Passenger rail transport includes widespread commuter networks in the major capital cities with more limited intercity and interstate networks. C. There are many forms of transport in Australia. D. The Australian mining sector relies on rail to transport its product to Australia's ports for export. E. There are more than 300 airports with paved runways. LESSON 2. READING Exercise 1. Read the text below and choose ONE word from the box to fill in each blank. public transport infrastructure prevent congestion obey The traffic problem is one of the common problems in metropolitan cities around the world. Cities like Delhi, Mumbai, Tokyo, Shanghai, Beijing, and other cities in the US and Europe face traffic (1) ________________ daily. congestion, or traffic jams. When traffic jams happen, cars that are stuck in the congestion continue to run their engines. This creates pollution and is a big problem. Pollution causes health problems for the people in cities and also hurts the environment. Some big cities around the world have found ways to help solve common traffic problems. In London, England, for example, drivers must pay a very high fee to drive into downtown areas. The government in Singapore also makes people pay large amounts of money to own a car. Because of this, it is too expensive for many Singaporeans to own a car. In places like Tokyo, buying a car is not too expensive for many people. However, finding a parking place is often almost impossible, and paying for parking can be very expensive. Since the public transportation system in Tokyo is very good, for many commuters, it is more convenient not to own a car. Reducing the number of cars in cities is helpfill. However, making it too difficult or too expensive to own a car is only one solution. Governments need to find other solutions to the problems of traffic and pollution as well. 1. What is one of the biggest problems that large cities have? A. light traffic B. pollution from cars C. unemployment D. lack of parking lots 2. Why is there traffic congestion in big cities? A. the population and the number of cars on the road increase B. cities can improve the number and size of their roads C. cars are stuck in the congestion D. paying for parking can be very expensive 3. What does pollution cause? A. benefits for the environment B. good public transportation system C. traffic jams D. health problems for the people in cities 4. The word “reducing” in paragraph 4 is closest in meaning to ___________? A. increasing B. improving C. decreasing D. growing 5. According to some cities, what is NOT the solution to help solve common traffic problems? A. drivers must pay a very high fee to drive into downtown areas B. people have to pay large amounts of money to own a car C. reducing the number of cars in cities 8. Have some people reported feeling homesick? ___________________________________________________________________________________ Exercise 5. Read the text and decide whether the following sentences are True (T) or False (F). Yesterday, on the way home from school, I saw an accident. A boy was run over by a taxi when he was riding his bicycle. The boy's leg was broken and it was bleeding badly. Someone there tried to stop the bleeding. They put pressure on it and held it tight. A man used his mobile phone to call the emergency service. Some minutes later, an ambulance arrived and sent the boy to the hospital. Two policemen came to the scene immediately. Some people told the police that the taxi driver was driving at a very high speed when the accident happened. Some others began talking about the traffic accidents these days and blamed the increasing number of accidents on the roads for careless driving and drunk drivers. 1. The writer saw an accident on the way home from school. 2. A boy was run over by a taxi when he was riding his motorbike 3. The boy's arm was broken and it was bleeding badly. 4. The boy was sent to the hospital in an ambulance. 5. Some people said that the taxi driver was driving at a very high speed when the accident happened. 6. Some people believed that careless driving and drunk drivers resulted in the increasing number of accidents on the roads. Exercise 6. Read and complete the sentences with words or phrases from the text. Traffic Jams Traffic jams in Viet Nam only frequently take place in Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City. Vietnamese people seem to be accustomed to traffic congestion, even miss it whenever they go to other places. There is no fixed rule for the time the traffic jams happen but it is worse during the rush hour when everyone is in a hurry to get to work or come back home. Apart from peak hours, the time between 9 a.m to 10 a.m and between 3 p.m to 4 p.m also witnesses long lines of vehicles, mainly motorbikes, struggling to get out of narrow streets. Whenever it rains, the traffic jam gets more terrible with the joining hand of flooding. Taxis are extremely hard to catch or wave during the downpour. However, it only takes about 30 minutes on average for a standstill and 2 hours to get through the worst, not really bad compared to that of other countries. 1. Traffic congestion in Viet Nam only frequently happens in ________________. 2. The traffic jam is worst during the ________________ when everyone is in a hurry to get to work or 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Exercise 3. Complete the sentences with suitable preposition: in, on, by. 1. We go to school _________ foot every day. 2. She went to the park _________ her mother’s car. 3. My family travelled to Phu Quoc _________ plane. 4. Don’t worry! Lan is getting here _________ a taxi. 5. We are quite busy, so our children go to school _________ bus. 6. They are _________ the train to pay a visit to their grandparents. 7. I want to keep fit, so I go to work _________ my bike. 8. Really? Are we _________ the most modern helicopter? 9. My father usually goes to work _________ car. 10. Last Friday I went to the countryside _________ motorbike. Exercise 4. Complete the sentences with a suitable word/ phrase in the box. take drive get in sail get on (x2) ride get out of fly board 1. I think we should _________ the bus more often to protect the environment. 2. Before _________ the train, passengers have to buy and show their tickets. 3. Tourists on vacation began to _________ the ship. 4. Jane used to _________ her bike to school when she was a student. 5. My children usually _________ a boat around the river in our hometown on summer holiday. 6. The drunk man _________ a taxi so fast that he caused an accident last night. 7. The FAA requires 1500 hours for a pilot to _________ a plane. It can be earned in two years. 8. After buying a cup of coffee, the man _________ the van and drove away. 9. Mandy stopped and _________ the car to take some nice sunset photos. 10. Paul arrived at the station quite late, so he had to run to the bus and _________ just before it started to leave. Exercise 5. Complete the sentences with SHOULD or SHOULDN'T. 1. You _________ stop and look both ways when you cross the road. take handlebars transport users pedestrians 1. I think I’ll ________________ a taxi to go home because I’m tired. 2. Children shouldn’t ride their bikes ________________. 3. ________________ should walk on the pavement or footpath. 4. You must always ride your bike with your hands on the ________________. 5. Road ________________ are not allowed to drink alcohol before driving. 6. When there are traffic ________________, it takes me longer to get to school. 7. Motorbikes are among the most common means of ________________ in Viet Nam. 8. A “green light” ________________ means you have to go. 9. We must ________________ traffic rules for our safety. 10. Please fasten your ________________ before the plane takes off. Exercise 8. Underline the correct answers. 1. We can buy a train ticket/fare from the machine at some stations. 2. A horse / zebra crossing is a type of pedestrian crossing. 3. The traffic rule is to keep on/to the right in Viet Nam. 4. Young men have the worst accident /incident records of all. 5. People should use public /common transport to reduce exhaust fumes. 6. Can we travel to Sa Pa on/by train? 7. How long/far is it from here to your school? 8. You should look/see right and left when you go across the road. 9. Cut/Reduce your speed please! 10. Don’t cross the road at/on a red light. Exercise 9. Circle the correct answers. 1. We should wait for the traffic lights _____________ before we cross the street. A. turn green B. turn red C. to turn green D. to turn red 2. Why do we have to _____________ the seatbelt in a car? A. tight B. fasten C. loose D. roll 3. Don’t forget to give a _____________ before you turn left or right. A. signal B. signature C. sign D. signing 4. The driver of the car _____________ stop for children to cross at the zebra crossing. A. can B. can’t C. mustn’t D. must 5. How _____________ is it from here to the nearest bus stop? A. long B. often C. far D. much
File đính kèm:
 bai_tap_tieng_anh_lop_7_global_success_chuong_trinh_hoc_ki_2.docx
bai_tap_tieng_anh_lop_7_global_success_chuong_trinh_hoc_ki_2.docx Chinh phục 4 kỹ năng tiếng Anh lớp 7 tập 2 Global2022.rar
Chinh phục 4 kỹ năng tiếng Anh lớp 7 tập 2 Global2022.rar

