Đề cương ôn tập kiểm tra giữa học kì 1 Tiếng Anh Lớp 11 Global Success - Năm học 2023-2024
Bạn đang xem tài liệu "Đề cương ôn tập kiểm tra giữa học kì 1 Tiếng Anh Lớp 11 Global Success - Năm học 2023-2024", để tải tài liệu gốc về máy hãy click vào nút Download ở trên.
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Đề cương ôn tập kiểm tra giữa học kì 1 Tiếng Anh Lớp 11 Global Success - Năm học 2023-2024
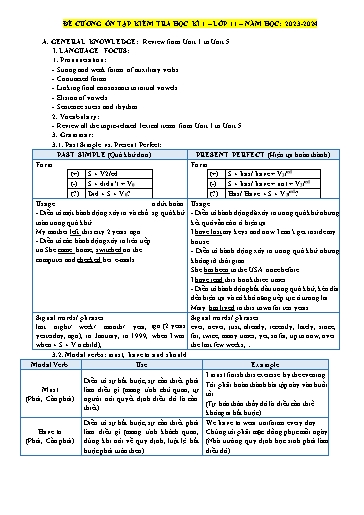
You should eat more vegetables. They Should Được dùng để đưa lời khuyên, đưa ra gợi are good for you. (Nên) ý hay ý kiến Bạn nên ăn nhiều rau hơn. Chúng tốt cho bạn. Mustn’t Dùng khi cấm một việc gì đó hay diễn We mustn’t touch it. (Không được) tả ý không được phép làm gì Chúng ta không được chạm vào nó. You don’t have to drive me home. I can Don’t/ Doesn’t take a taxi. Diễn tả một việc gì đó là không cần have to Bạn không cần phải lái xe đưa tôi về thiết (Không cần phải) nhà. Tôi có thể bắt taxi. 3.3. Stative Verbs and Linking Verbs: a) Stative verbs in the continuous form: (Động từ trạng thái ở hình thức tiếp diễn) - Động từ trạng thái mô tả một tình trạng, trạng thái thay vì một hành động. - Chúng thường ám chỉ suy nghĩ và ý kiến, cảm giác và cảm xúc, giác quan, và sự sở hữu,. - Chúng thường không được dùng trong các thì tiếp diễn. Use Example Stative verbs often refer to: Thoughts and opinions agree, believe, doubt, expect, guess, imagine, know, mean, Động từ chỉ suy nghĩ và quan điểm recognize, remember, suspect, suppose, think, understand, know Feelings and emotions dislike, detest, hate, like, love, prefer, want, wish, need, enjoy, Động từ chỉ tình cảm, cảm xúc satisfy Senses and perceptions feel, hear, see, smell, taste, look, sound, seem, appear, be Động từ chỉ giác quan, nhận thức Possession and measurement belong to, have, own, consist of, possess, include, involve, measure, Động từ chỉ sở hữu và đo lường weigh * Notes: Stative Verbs Action Verbs Verbs Meaning Example Meaning Example Nghĩ rằng Suy nghĩ Think Cho rằng He thinks he’s really clever. Cân nhắc I’m thinking about his offer. Tin rằng Xem xét Taste Có vị This tastes salty. Nếm Why is he tasting the soup? Có Sở Ăn, uống, Have He has two houses She’s having a shower. hữu tắm,.. Cảm thấy, Feel The silk shirt feels soft. Sờ, chạm Ann is feeling the cat’s fur. cảm giác Hiểu I see what you mean! See Nhìn Do you see those birds? Gặp I’m seeing Paula tonight. thấy Smell Có mùi Your perfume smells of Ngửi She is smelling the roses. apples. Enjoy Thích I enjoy good films. Tận hưởng I’m enjoying my holiday now. Trông, nhìn Look He looks tired today. Nhìn He is looking at the painting. có vẻ 1. allow (cho phép) 13. enjoy (thích) 26. prevent (ngăn chặn) 2. avoid (tránh) = like/ feel like/ love/ fancy/ 27. propose (đề nghị/ đề xuất) 3. admit (thừa nhận) prefer 28. quit (nghỉ, thôi) = give up 4. advise (khuyên nhủ) 14. encourage (khuyến khích) 29. recall (nhớ) 5. appreciate (đánh giá cao) 15. forbid (cấm) 30. recollect (nhớ ra, hồi tưởng) 6. complete (hoàn thành) 16. finish (hoàn thành) 31. recommend (đề xuất/ gợi ý) 7. consider (xem xét, cân 17. imagine (tưởng tượng) 32. regret (hối hận vì đã làm gì) nhắc) 18. involve (bao gồm) 33. risk (liều) 8. continue (tiếp tục) 19. include (bao gồm) 34. stop (dừng làm gì/ ngăn = go on/ keep on/ carry on 20. mention (đề cập) cản) 9. delay (trì hoãn) 21. mind (phiền, ngại) 35. spend (sử dụng thời gian) 10. deny (từ chối) 22. miss (nhớ, bỏ lỡ) 36. suggest (đề nghị) 11. discuss (thảo luận) 23. permit (cho phép) 37. can’t stand/bear 12. dislike (không thích/ ghét) 24. postpone (trì hoãn) 38. can’t help/ resist = hate/ detest 25. practice (luyện tập) Common prepositional combinations followed by gerunds (V-ing) (Một số cụm giới từ được theo sau bởi V-ing) - be excited about doing sth - keep sb from doing sth - be interested in doing sth - be worried about doing sth - prevent sb from doing sth - - believe in doing sth - complain about/ of doing sth prohibit sb from doing sth - participate in doing sth - dream of/ about doing sth - stop sb from doing sth - succeed in doing sth - talk about doing sth - instead of doing sth - think about/of doing sth - take advantage of doing sth - be accused of doing sth - take care of doing sth - be capable of doing sth - be tired of/ from doing sth - be guilty of doing sth - be fond of doing sth - apologize for doing sth - be accustomed to doing sth - insist on doing sth - blame sb for doing sth - be/ get used to doing sth - focus on doing sth - forgive sb for doing sth - in addition to doing sth - concentrate on doing sth - have an excuse for doing sth - be committed to doing sth - be keen on doing sth - have a reason for doing sth - be devoted/ dedicated to doing sth - be responsible for doing sth - look forward to doing sth - thank sb for doing sth - object to doing sth - be opposed to doing sth - prefer doing sth to doing sth 3.5. Present participle and Past participle clauses PRESENT PARTICIPLE PAST PARTICIPLE HIỆN TẠI PHÂN TỪ QUÁ KHỨ PHÂN TỪ Hình thức: V-ing Hình thức: V-ed/ V3 - Mang nghĩa chủ động - Mang nghĩa bị động - Có chức năng như một tính từ - Có chức năng như một tính từ • People will have limited privacy due to cameras installed everywhere in the city. • People become worried because their personal information might not be protected. B. PRACTICE: I. Circle A, B, C or D to indicate the word whose underlined part differs from the other three in pronunciation in each of the following questions. 1. A. issue B. disease C. climate D. footprint 2. A. awareness B. behavior C. relation D. exchange 3. A. confident B. official C. current D. cultural 4. A. generation B. ingredient C. greenhouse D. argument 5. A. community B. temperature C. pollutant D. tmosphere 6. A. propose B. respond C. follow D. honour 7. A. gender B. footstep C. dweller D. belief 8. A. public B. urban C. current D. upset II. Circle A, B, C or D to indicate the word that differs from the other three in the position of the primary stress in each of the following questions. 1. A. consequence B. leadership C. atmosphere D. pollution 2. A. poster B. workshop C. exchange D. teamwork 3. A. community B. television C. experience D. development 4. A. understand B. volunteer C. represent D. qualify 5. A. confident B. practical C. successful D. excellent 6. A. surprise B. promote C. apply D. manage 7. A. nutritious B. prosperous C. liveable D. critical 8. A. traditional B. renewable C. sustainable D. beneficial III. Circle A, B, C or D to indicate the correct answer to each of the following questions. 1. Just 15 minutes of daily ___________ can add three more years of life A.smoking B. reading C. routines D. exercise 2. Gen Z can ___________ very easily to changes as they are creative and adventurous. A.lead B. contribute C. adapt D. reply 3. I don’t cook well, so I just whip up some easy Vietnamese _______, such as: spring rolls or fried rice. A.minerals B. nutrition C. recipes D. ingredients 4. 30 minutes is enough time to use social media because the screens of electronic devices _______ blue lights. A.give up B. give off C. take in D. take up 5. During the Second World War, bread ___________ usually brown and whole wheat due to a shortage of white flour. A.was B. has been C. had been D. is 6. My grandparents encourage me to __________ my dream to become an engineer. A.quit B. follow C. improve D. awaken 7. Breadwinning and childcare are the ________ roles of men and women in society. A.respecting B. respective C. respectable D. respectful 8. My parents’ imposition ________ no difference to my decision of choosing the future career. A.gives B. pays C. takes D. makes 9. The city government is _____________ in the development of green spaces in our neighborhood. A.investing B. increasing C. operating D. controlling 10. With more parks and gardens, the air quality will improve, and it will ___________ the quality of life for everyone. A.reduce B. enhance C. sustain D. construct 11. These smart technologies will help save energy, reduce air ___________ , and fight climate change. A.footprint B. pressure C. pollution D. warming 12. Smart street infrastructure with sensor technology will provide information _________ faster, cheaper, and better decision-making 34. __________ in the 15th century, this house is the oldest in this area. A.To build B. Built C. Building D. Build 35. The leaflets ________ by environmental organizations aim to raise awareness of the dangers of deforestation. A.distribute B. distributed C. distributing D. to distribute 36. __________ in the rocking chair, the old woman looked at the kids in her yard. A.Sitting B. Sat C. Sit D. Sits 37. The child stood at the wall ____________ a picture. A.paint B. painted C. paints D. painting 38. Each student __________ complete his/her homework before going to class because it’s a rule. A.ought to B. has to C. must D. should 39. Different generations _________ agree on everything, but it is important to participate in open-minded discussions. A.don’t have to B. can’t C. mustn’t D. have to 40. When discussing generational differences, we ___________ generalize or stereotype entire generations. A.should B. have to C. don’t have to D. shouldn’t IV.Read the following text and choose the best answer to fill in the blanks. Coal, oil, and natural gas supply modern civilization (1) __________ most of its power. However, not only are supplies of these fuels limited, but they are a major source of pollution. If the energy demands of the future are to be met without seriously harming the environment, existing (2) __________ energy sources must be improved or further explored and developed. These include nuclear, water, solar, wind, and geothermal power, as well as energy from new, (3) __________ types of fuels. Each of these alternatives, (4) __________, has advantages and disadvantages. Nuclear power plants efficiently produce large amounts of electricity without polluting the atmosphere; however, they are costly to build and maintain, and they pose the daunting problem of (5) __________ to do with nuclear wastes. Hydroelectric power is inexpensive and environmentally safe, but impractical for communities located far from moving water. Harnessing energy from tides and waves has similar drawbacks. Solar power holds great promise for the future but methods of collecting and – concentrating sunlight are as yet inefficient as are methods of harnessing wind power. 1. A. on B. for C. with D. of 2. A. available B. alternative C. man-made D. natural 3. A. non-polluting B. pollution C. polluted D. polluting 4. A. so B. instead of C. additionally D. however 5. A. why B. when C. what D. who V. Read the following passage and circle A, B, C, or D to indicate the correct answer to each of the questions. Where smart cities were once regarded purely as a vision of the future, they are now becoming a reality in numerous urban centres across the globe. From Dubai, Singapore, Amsterdam, Copenhagen, and Madrid to Southampton in the UK, we’re already beginning to see smart cities provide inhabitants with improved living conditions, easier mobility and cleaner, safer environments, by using cloud computing to power services. But as with all public sector initiatives, smart city services need to be delivered as cost effectively as possible to minimise the taxpayer burden. Often, key decision makers are met with obstacles when it comes to deploying smart services, preventing smart cities initiatives from reaching their full potential – or worse, blocking them altogether. Central to the functioning of most ‘normal’ city ecosystems is the underlying data they run on. Regardless as to whether that data is stored on local servers or using cloud storage, when that data is fragmented or incomplete, identifying emerging trends for strategic planning and cost reduction becomes extremely difficult – and because of this, authorities have to adopt an entirely reactive approach. Conversely, in a smart city environment, connected sensors forming an Internet of Things (IoT) provide valuable data for analysis and, in turn, insight into the specific city’s behavioural trends. With this level of information, services can be optimised to reduce costs and risk, increase urban 5. Scientists think it is unlikely that any species will actually become extince as a consequence of the oil spill. Agood result B. effective action C. timely decision D. bad result VIII. Identify the mistake in each of the following questions. 1. She (A) should go (B) out late (C) at night because of danger. 2. The accident (A) looked (B) seriously but (C) fortunately nobody (D) was injured. 3. (A) Let’s stop (B) to watch so much TV so that we can (C) read or (D) go out instead. 4. He postponed (A) to make a decision (B) till it was (C) too late to do (D) anything. 5. (A) Inventing by an Indiana housewife in 1889, the first (B) dishwasher (C) was driven by a steam (D) engine. 6. (A) Listened (A) to (B) his favorite songs, Max (C) checked all the papers and (D) signed the posters. IX. Rewrite the following sentences without changing their original meaning or do as directed. 1. She was talking to her friend and forgot everything around her. (Using participles) _________________________________________________, she forgot everything around her. 2. Since we watch the news every day we know what's going on in the world. (Using participles) ______________________________________________, we know what’s going on in the world. 3. The man was sitting in the cafe. He was reading a paper. (Using participles) The man _______________________________________________________________________ 4. The event is organised by our team and will surely be a great success. (Using participles) ______________________________________________, the event will surely be a great success. 5. The car was taken to the garage. It was repaired within an hour. ________________________________________________, the car was repaired within an hour. 6. She didn’t say a word as she left the room. (Using gerunds) She left the room without__________________________________________________________ 7. Could you turn the radio down? (Using gerunds) Would you mind _________________________________________________________________ 8. It is very interesting to dance around the campfire. (Using gerunds) _________________________________________________________________ is very interesting. 9. I would like to do the laundry every day. (Using gerunds) I am interested ___________________________________________________________________ 10. My sister usually makes cakes in her free time. (Using gerunds) My sister’s hobby is ________________________________________________________________ 11. The thick fog made it impossible for me to drive to work. (Using gerunds) The thick fog prevented ____________________________________________________________ 12. He/ start/ work/ a manager/ this company/ 3 months/ ago. (Make a complete sentence) _________________________________________________________________________________ 13. Alexander Fleming/ discover penicillin/ 1928, / which/ lead/ the introduction of antibiotics. (Make a complete sentence) _________________________________________________________________________________ 14. Since/ my grandfather/ young boy,/ he/ do regular exercise/. (Make a complete sentence) _________________________________________________________________________________ 15. Her daughter/ suffer/ heart disease/ since/ she/ born (Make a complete sentence) _________________________________________________________________________________ -The end-
File đính kèm:
 de_cuong_on_tap_kiem_tra_giua_hoc_ki_1_tieng_anh_lop_11_glob.docx
de_cuong_on_tap_kiem_tra_giua_hoc_ki_1_tieng_anh_lop_11_glob.docx

